Downloading, building, and running the node using Docker
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Step 1: Download the node
- Step 2: Create directories and place the files
- Step 3: Start the node
- Step 4: Get the certificate
- Step 5 (optional): Automated updates for node with Watchtower
- How to stop the node?
- How to check, if my node works?
- What do I need to do if something goes wrong?
Introduction
We recommend you to use the simple way of building the node using the Docker image. Follow the steps below.
Step 1: Download the node
To download the node using Docker:
-
Ensure you have Docker installed on your machine.
-
If not, refer to Docker Installation Guide.
Hint:
If you don't use
rootaccount, run the following command to ensure you belong the user groupdocker:$ groupsIf you don't belong to the user group
docker, run the following command:$ sudo usermod -aG docker
Step 2: Create directories and place the files
Hint
You can create an additional directory named
thepower, for example, and placedbandlogas subdirectories there.
To create directories for files:
-
Go to your working directory using the following command:
cd /opt/thepower -
Create
dbandlogdirectories in your working directory (/opt/thepower, for instance) using the following command:mkdir {db,log} -
Place
genesis.txtandnode.confignear these directories using the following commands:cp ~/tea_ceremony_directory/node.config /opt/thepower/node.configcp ~/tea_ceremony_directory/genesis.txt /opt/thepower/genesis.txt
Before the Tea Ceremony, the client listens to the ports that will be used on this particular chain and the server checks, if those ports are available. The Ceremony itself starts right after this check. If there will be only a ceremony token specified, without the personal one, you will not be able to participate in Tea Ceremony.
If you're connecting to the Ceremony that has already ended, the Tea Ceremony client will save the node.config file. If the node.config consisted only of a private key, the Tea Ceremony client will add an actual configuration right into this file. If there is something else specified in node.config, the configuration will be saved in node_example.config. After that you need to add your node private key to this file.
The private key you get with the node.config file cannot be restored, if you lose it. Please, store it securely: place a backup onto your local machine.
Step 3: Start the node
To start the node from Docker, run:
docker run -d \
--name tpnode \
--restart unless-stopped \
--mount type=bind,source=/opt/thepower/db,target=/opt/thepower/db \
--mount type=bind,source=/opt/thepower/log,target=/opt/thepower/log \
--mount type=bind,source=/opt/thepower/node.config,target=/opt/thepower/node.config \
--mount type=bind,source=/opt/thepower/genesis.txt,target=/opt/thepower/genesis.txt \
-p 1800:1800 \
-p 1080:1080 \
-p 1443:1443 \
thepowerio/tpnode
The commands
-p 1800:1800 \
-p 1080:1080 \
-p 1443:1443 \
specify all necessary local ports. In this example ports api, apis, and tpic are used. Specify the port of your chain from node.config file.
where:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
docker run -d | This command starts Docker in the background |
--name tpnode | This command specifies the name (optional) |
--restart unless-stopped\ | Similar to always, except that when the container is stopped (manually or otherwise), it is not restarted even after Docker daemon restarts |
--mount type=bind,source="$(pwd)"/db,target=/opt/thepower/db | Path to the database. Bound to Docker. /opt here is mandatory, because it is the path inside the container. |
--mount type=bind,source="$(pwd)"/log,target=/opt/thepower/log | Path to log files. Bound to Docker. /opt here is mandatory, because it is the path inside the container. |
--mount type=bind,source="$(pwd)"/node.config,target=/opt/thepower/node.config | Path to your node.config file. Bound to Docker. /opt here is mandatory, because it is the path inside the container. |
--mount type=bind,source="$(pwd)"/genesis.txt,target=/opt/thepower/genesis.txt | Path to your genesis.txt. Bound to Docker. /opt here is mandatory, because it is the path inside the container. |
-p 1800:1800 -p 1080:1080 -p 1443:1443 | These commands specify all necessary local ports. In these examples ports api, apis, and tpic are used. You can specify any port in node.config file. |
thepowerio/tpnode | Path to Docker image. |
Step 4: Get the certificate
Obtain the SSL certificate for your node and place it into the db directory.
Step 5 (optional): Automated updates for node with Watchtower
If configured, every 24 hours the Watchtower will check if a new version of The Power Node is available and update it if so.
If you haven't configured automatic updates, DO NOT follow this step.
Use this guide instead.
Start a Watchtower container to automatically update node when a new version is available:
docker run -d \
--name watchtower \
--restart unless-stopped \
-e WATCHTOWER_CLEANUP=true -e WATCHTOWER_TIMEOUT=60s \
-v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock \
containrrr/watchtower
How to stop the node?
To stop the node, run:
-
docker stop tpnode -
docker rm tpnode -
docker rmi thepowerio/tpnode
How to check, if my node works?
To check, if your node works, run:
curl http://your_node.example.com:1080/api/node/status | jq
where:
your_node.example.com— your node address;1080— port, that your node uses forapi.
Replace the example parameters with the ones you need.
What do I need to do if something goes wrong?
If something goes wrong, go to the log folder, and read the logs. If there are errors, write to Power Ecosystem Telegram chat: https://t.me/thepower_chat.
Troubleshooting
-
You get the following error:
===> Failed to boot tpnode for reason {{{badmatch,undefined},
[{nodekey,get_priv,0,
[{file,
"/home/thepower/tpnode/apps/tpnode/src/nodekey.erl"},
{line,26}]},
{tpic2,certificate,0,
[{file,
"/home/thepower/tpnode/apps/tpic2/src/tpic2.erl"},
{line,196}]},
{tpic2,
'-childspec/0-fun-0-',2,
[{file,
"/home/thepower/tpnode/apps/tpic2/src/tpic2.erl"},
{line,217}]},
{tpic2,childspec,0,
[{file,
"/home/thepower/tpnode/apps/tpic2/src/tpic2.erl"},
{line,229}]},
{tpnode_sup,init,1,
[{file,
"/home/thepower/tpnode/apps/tpnode/src/tpnode_sup.erl"},
{line,88}]},
{supervisor,init,1,
[{file,"supervisor.erl"},
{line,295}]},
{gen_server,init_it,2,
[{file,"gen_server.erl"},
{line,374}]},
{gen_server,init_it,6,
[{file,"gen_server.erl"},
{line,342}]}]},
{tpnode,start,[normal,[]]}}Reason
You don't have
genesis.txtandnode.configfiles.Solution
Start the Tea Ceremony client BEFORE starting the node. It will get proper
genesis.txtandnode.config. -
You get the following error when starting the Tea Ceremony client:
~/tpnode# ./teaclient DEE570BD76F3
-bash: ./teaclient: Permission deniedReason
Probably, you haven't changed
teaclientfile mode to executable.Solution
Change
teaclientfile mode to executable by running the following command:chmod +x tea* -
You get the following error when starting the Tea Ceremony client:
~# ./teaclient -n demonode05 DEE570BD76F3
ceremony client connecting to tea.thepower.io:443
Server rejects connection, reason: bad_tokenReason
Token
DEE570BD76F3has been used by another user.Solution
Get the new token from the Telegram bot.
-
You get the following error when starting the Tea Ceremony client:
ceremony client connecting to knuth.cleverfox.ru:1436
=WARNING REPORT==== 19-Oct-2022::14:32:54.056133 ===
Description: "Authenticity is not established by certificate path validation"
Reason: "Option {verify, verify_peer} and cacertfile/cacerts is missing"
Server rejects connection, reason: you_are_lateReason
You are late for the tea ceremony.
Solution
Stick to the bot recommendations and don't be late.
-
You see different ports displayed in server control panel and written in firewall rules.
Reason
Problems with ports.
Solution
Check your
iptablesrules:iptables -L -nvFind the rules for all three ports among the entries:
- If the rules are absent, please contact or tech support in our Telegram chat.
- If you've found a corrupted port, try to recreate rule using the server control panel.
warningThe Power Ecosystem is not responsible for the result of actions described below! These actions can lead to loss of access to the server.
Another way of addressing the problem is to:
-
Save the rules into a file using the following command:
iptables-save -f iptables.save -
Edit the corrupted port:
vim iptables.save -
Restore the rules from the file:
iptables-restore iptables.save
-
You see the following error:
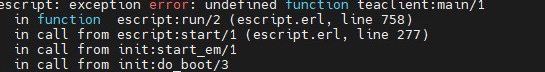
Reason
Wrong Erlang version is installed.
Solution
Install the recommended Ubuntu version, or try to install right Erlang version using the third party repositories or the source code.