Testnet Campaign Flow (Phase 2)
Table of Contents
Introduction
This simple guide will help you participate in The Power testnet campaign.
Please, turn off the firewall before you start working with the node.
Prerequisites for a node
Hardware
| CPU cores | Memory | Hard disk | Network |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 4 GB or more | Minimum: 40 GB, SSD preferred | 100 Mbit/s |
Software
| OS | Erlang version | Eshell version | Docker version | Server |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ubuntu 22.04 | 24.3 | 10.4 | latest (20.10.18 as of September 2022) | Virtual machine |
You need to have a clear server to work with your node. If you have done any experiments before, please delete the previous builds.
If you use other versions of Ubuntu, you'll have to resolve the Erlang dependencies manually.
What do I need to participate in testnet campaign?
To participate in ThePower testnet campaign you need to:
Step 1: Learn
Learn what is a testnet in DCloud. This guide will help you understand what ThePower Testnet is.
Step 2: Get IP addresses and DNS
You need to have a public IP address to take part in the testnet campaign. You can register a DNS for your server, if you want. The word "domain" will be used in the text below with the meaning of "domain", or of "IP address". The Power DCloud team is not responsible for assignment or registration of IP addresses or DNS.
Here you have the following options:
-
You may have your own domain name (recommended).
-
You may use the VPS-generated domain name. You can check your domain name at your VPS. Here are the examples for Hetzner and Scaleway:
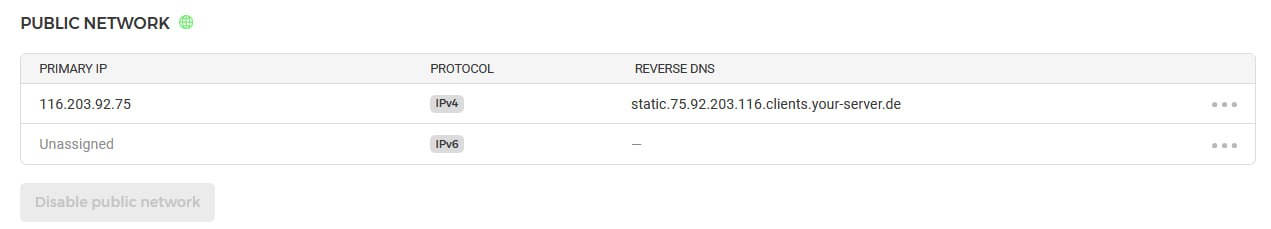

-
You may use free services, like FreeDNS. You can also use the following hosting services from the list below:
-
If none of the options above didn't work, submit a request for a domain name in our Discord chat.
NoteThis option takes much more time, then the others, due to manual proccessing of submitted requests by the team.
Step 3: Set up your environment
Before start working with the node you need to set up your environment by installing Erlang, getting tpcli, and keys. Follow the steps below:
-
To install Erlang, run:
apt -y install erlang-base erlang-public-key erlang-ssl docker-compose jqNote
You need to install
erlang-public keyanderlang-ssl. Otherwise, Erlang will not operate properly! -
Get the power CLI:
-
Get the power cli by running the following command:
sudo wget https://tea.thepower.io/tp -O /usr/local/bin/tp -
Change the
tpfile mode to executable by running the following command:sudo chmod a+x /usr/local/bin/tp
-
-
Create
/opt/thepower/db/certand/opt/thepower/logdirectories by running the following command:mkdir -p {/opt/thepower/db/cert,/opt/thepower/log} -
Go to
/opt/thepowerby running the following command:cd /opt/thepower -
Generate private key by running the following command:
tp --genkey --ed25519As a result of this action, you will get the
tpcli.keyfile. This file contains your private and public keys. Here is an example of this file. DON'T use the keys specified in this example:cat tpcli.key
{privkey,"302E020100300506032B6570042204204B1F52826447066469E7DBCA4E95CB0A03A2998D268C27885364D4AD7B7B0A8E"}.
{pubkey,"302A300506032B6570032100667C84FB1195C73F97AE14430C2024490C0EA6490F6EC0C1DE3FAEB4B6B32251"}.cautionYou may share your public key when necessary, but never share your private key.
Backup the file and continue.
-
Download the
node.configfile using the link. Here is the example of code:node.config{tpic,#{peers => [],port => 1800}}.
% ====== [ here is an example of configuration ] ======
{discovery,#{addresses =>[
#{address => "replace_with_your_hostname", port => 1800, proto => tpic},
#{address => "replace_with_your_hostname", port => 1443, proto => apis},
#{address => "replace_with_your_hostname", port => 1080, proto => api}
]}}.
{replica, true}.
{hostname, "replace_with_your_hostname"}.
{upstream, [
"Insert_here_your_upstream_link1",
"Insert_here_your_upstream_link2"
]}.
% ======= [ end of example ] =========
{dbsuffix,""}.
{loglevel, info}.
{info_log, "log/info.log"}.
{error_log, "log/error.log"}.
{debug_log, "log/debug.log"}.
{rpcsport, 1443}.
{rpcport, 1080}.cautionYou need to replace the following:
-
#{address => "replace_with_your_hostname", port => 1800, proto => tpic},
#{address => "replace_with_your_hostname", port => 1443, proto => apis},
#{address => "replace_with_your_hostname", port => 1080, proto => api} -
{hostname, "replace_with_your_hostname"}. -
"Insert_here_your_upstream_link1", "Insert_here_your_upstream_link2". The links are obtained from The Power DCloud bot.
NoteUse this guide for more information on
node.config.NoteThe first upstream node in the link must be active. Otherwise, the
node.configwill not work properly.You can check the upstream node status by running the following command:
curl -s http://upstream_host:1080/api/node/status | jq .resultIf the command returns
okit means that no problems were discovered. If there is an error, then change the upstream links order innode.configfile. -
-
Run the following command:
grep priv tpcli.key >> node.configcautionThis and the following steps are crucial because you will NOT be able to start your node without
node.configfile. You can find more information about these files here.
Step 4: Set up SSL
Follow the steps below to set up SSL:
-
Ensure that you use
rootaccount. It is necessary for further steps. -
Install
acme.shby running the following command. Please, specify your real e-mail address:apt-get install socat
curl https://get.acme.sh | sh -s email=my@example.comwhere
my@example.com— your active e-mail. Make sure, you have replaced it with your e-mail address. -
Log out of the system.
-
Log in again.
-
Obtain the certificate. To do this, run the following command:
acme.sh --issue --standalone -d your_node.example.comwarningyour_node.example.comis an example. Replace it with your node link. -
Install the certificate by running the following command:
acme.sh --install-cert -d your_node.example.com \
--cert-file /opt/thepower/db/cert/your_node.example.com.crt \
--key-file /opt/thepower/db/cert/your_node.example.com.key \
--ca-file /opt/thepower/db/cert/your_node.example.com.crt.ca.crtwarningyour_node.example.comis an example. Replace it with your node link.After you've installed the certificate, you can get the certificate status by running the following command:
acme.sh --info -d your_node.example.comwhere
your_node.example.com— your node address link. Replace it with your node link.
Step 5: Start a seed node
Follow the steps below to start your seed node.
Step 1: Set up your environment
-
Go to
/opt/thepower:cd /opt/thepower -
Download
docker-compose.ymlfile under the link. Here is the example of code:
version: "3.3"
services:
tpnode:
restart: unless-stopped
container_name: tpnode
cap_add:
- NET_ADMIN
devices:
- /dev/net/tun
image: thepowerio/tpnode
volumes:
- type: bind
source: /opt/thepower/node.config
target: /opt/thepower/node.config
read_only: true
- type: bind
source: /opt/thepower/db
target: /opt/thepower/db
- type: bind
source: /opt/thepower/log
target: /opt/thepower/log
network_mode: 'host'
watchtower:
restart: unless-stopped
container_name: watchtower
image: containrrr/watchtower
volumes:
- /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock
command: --interval 3600 --cleanup
This file also allows watchtower to automatically update the node.
By starting the node we assume that
node.config,dbandlogdirectories,- SSL keys, and
docker-compose.yml
are present and stored in /opt/thepower/ like described in Docker manual.
The following tree describes the directories and files in them:
/opt/thepower/
├── db
│ └── cert
│ ├── hostname.crt
│ ├── hostname.crt.ca.crt
│ └── hostname.key
├── log
├── docker-compose.yml
├── node.config
└── tpcli.key
We assume you have the same tree.
hostname here is an example. Please, replace it with the hostname specified in your node.config file.
Step 2: Start the node
To start the node:
-
Ensure, that you are in
/opt/thepowerdirectory. If not, run:cd /opt/thepower -
Run the following command:
docker-compose up -d
How to check, that the node works?
Check, if your node work properly by running the following command:
curl https://your_node.example.com:1443/api/node/status | jq
The command above returns .json with actual info about the node.
https is essential for normal operation of your node. Though, if you experience problems when connecting to your node via https, you can also check your node status via http using the following command:
curl http://your_node.example.com:1080/api/node/status | jq
You can also look through the logs by running the following command:
docker logs tpnode
How to stop the node?
- Ensure, that you are in
/opt/thepowerdirectory. If not, run:
cd /opt/thepower
- Run the following command:
docker-compose down
Node update
Your node will be updated automatically.
After you start a node, please, send your node link to RoverBot. Otherwise, you won't get points.